

While this type of result can be produced in a number of ways, it feels much cleaner using the MOD function to get a whole number remainder. This is the command: codeALTER TABLE tablename ALTER COLUMN columnname TYPE newdatatype /codeThe problem is that there are a number of restrictions. You could then define the training and test group using these simple numbers. One approach would be to divide each User ID by 3 using the modulo operation MOD(, 3) which would produce one of the 3 different remainders (0, 1, and 2) for each of the users. So why is this valuable? Think about creating training and testing bins for an experiment that were a) replicable and b) more randomly selected than just the splitting my (ordered) dataset into two parts by a date cutoff. The MOD command in Redshift lets you perform this function MOD(3,2) will equal 1. 3/2 gives us a remainder of 1 - this would be the modulus. Modulo math is all about determining the remainder of dividing two numbers. Modulo math is usually reserved for more advanced programming languages but can be useful inside of SQL as well. SELECT catid, catname FROM category WHERE mod ( catid, 2 ) = 1 ORDER BY 1, 2 catid There are so many other uses for row numbers when trying to clean or organize your data based on some ordinal parameter. If you want to see the most recent transaction for each customer for each product they’ve bought, just partition by both customer and the product, and your row numbering will restart with each new customer/product combination. Then filter your results to only include the rows that are in the position you care about - in this case, 1. Here we can assign an order to the transactions, grouped however you choose (in this case, by customer) and ordered however you choose (in this case, by transaction date descending, so the most recent orders for each customer are the same number: 1). The more elegant way is to use the ROW_NUMBER function. With no single date or date range to attach to all customers, we could find the most recent transaction date for each customer and then join the same transactions table to itself where the transaction date equals the customer’s most recent transaction date and the customer ID matches. We want the most recent purchase for each customer, even if it didn’t happen today. Think about customers with multiple purchases.
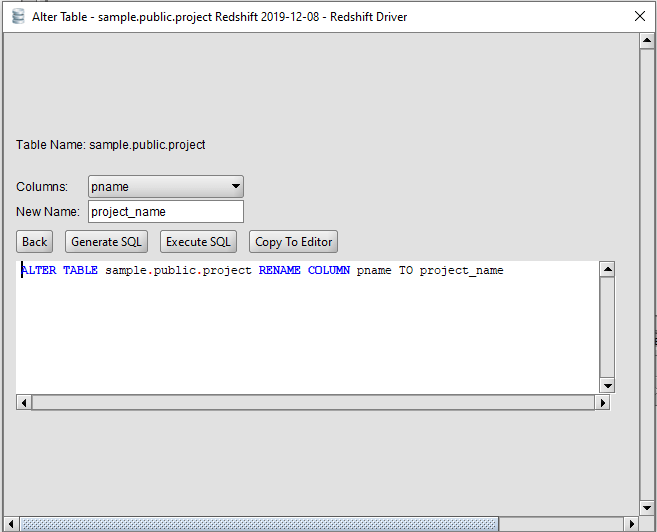
#REDSHIFT ALTER TABLE RENAME TAKES FOREVER FULL#
SHOW FULL PROCESSLIST while waiting for the FLUSH to complete (if there's a delay) will give you an idea of things that might get in the way of the rename operation, and you can safely KILL the flush if you need to.SELECT salesid, sellerid, qty, ROW_NUMBER () OVER ( PARTITION BY sellerid ORDER BY qty asc ) AS row FROM winsales ORDER BY 2, 4 salesid

so it gives you a good test of what to expect and would be a good idea to run first, since it's typically going to make the actual rename operation slightly shorter by leaving less work for the rename to do. the table is automatically reopened by the next statement that accesses it. If you are able to execute a FLUSH TABLES table_name statement and have it return within a few seconds, that should serve as confirmation that the rename operation will complete in a similar amount of time, since it will need the same locks in order to remove any entries in the query cache related to the table, close the table, and clean up some internal structures like the table share object. You can't alter columns with default values. You can't decrease the size less than maximum size of existing data. The major delay you could see will come from other sessions preventing the RENAME from starting because the locks can't be immediately required. In AWS Redshift is now possible to alter ONLY VARCHAR column but under these conditions: You can’t alter a column with compression encodings BYTEDICT, RUNLENGTH, TEXT255, or TEXT32K. Note that's a link to the 5.0 documentation, and the 5.1, 5.5, 5.6, and 5.7 all have the same information. If you use ALTER TABLE tbl_name RENAME TO new_tbl_name without any other options, MySQL simply renames any files that correspond to the table tbl_name without making a copy.
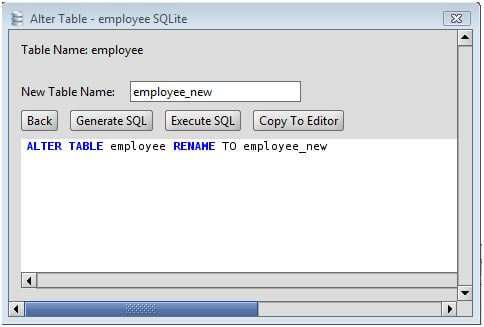
Renaming a table acquires a metadata lock on the table which requires that no statements be running against the table, no transactions have row locks, and no transactions are holding on to consistent snapshots of any MVCC versions of the table.Įither style of RENAME operation will attempt to acquire the metadata lock and subsequently-started statement impacting the table will block, waiting for the pending metadata lock. RENAME TABLE t1 TO t2 ĪLTER TABLE t1 RENAME TO t2 # as long as no other options to ALTER are also specified There are two statements that perform an equivalent operation. Renaming a table in MySQL does not require a temporary table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
